What Is the Only South American Country to Have Coastlines on the Pacific and the Caribbean?
 | |
| Continent | South America |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 4°00′N 72°00′W / iv.000°Northward 72.000°West / iv.000; -72.000 Coordinates: 4°00′North 72°00′West / 4.000°N 72.000°W / four.000; -72.000 |
| Area | Ranked 25th |
| • Total | ane,141,748 kmii (440,831 sq mi) |
| • Land | 91.2% |
| • H2o | 8.8% |
| Coastline | 3,208 km (ane,993 mi) |
| Borders | Full land borders: 6,672 km2 (2,576 sq mi) Venezuela: two,341 km Brazil: 1,790 km Peru i,494 km Republic of ecuador 708 km Panama 339 km |
| Highest betoken | Pico Cristobal Colon 5,775 metres (18,947 ft) |
| Lowest point | Pacific Ocean 0 metres (0 ft) |
| Longest river | Magdalena River 1,528 km (949 mi) |
| Largest lake | Lake Tota 55 km2 (21 sq mi) |
| Exclusive economic zone | 808,158 kmtwo (312,032 sq mi) |
The Republic of Republic of colombia is situated largely in the northwest of South America, with some territories falling inside the boundaries of Central America. It is bordered to the northwest by Panama; to the due east past Venezuela and Brazil; to the south by Republic of ecuador and Peru;[1] and it shares maritime limits with Costa rica, Nicaragua, Republic of honduras, Jamaica, the Dominican Republic, and Haiti.[2] [3]
Colombia has a land size of 1,141,748 km2 (440,831 sq mi) and it is the 25th largest nation in the world and the fourth-largest country in Southward America (after Brazil, Argentina, and Peru).[4] Colombia's population is not evenly distributed, and most of the people live in the mountainous western portion of the state equally well every bit along the northern coastline; the highest number live in or near the upper-case letter metropolis of Bogotá. The southern and eastern portions of the land are sparsely inhabited, consisting of tropical rainforest, and inland tropical plains that comprise large estates or big livestock farms, oil and gas production facilities, small farming communities, and indigenous tribes with their territories. Colombia has the 35th largest Exclusive Economic Zone of 808,158 kmtwo (312,032 sq mi).
Main [edit]
Colombia commonly classifies its geography into five natural regions, from the Andes mountain range, a region shared with Ecuador, Venezuela; the Pacific Ocean coastal region, shared with Panama and Ecuador; the Caribbean Bounding main coastal region, shared with Venezuela and Panama; the Llanos (plains), shared with Venezuela; to the Amazon Rainforest region shared with Venezuela, Brazil, Peru and Republic of ecuador. Republic of colombia is the just South American land that has coastline on both the Atlantic and Pacific oceans.
The Globe Factbook does not differentiate betwixt Amazon region of Colombia (predominantly jungle) and the Orinoquia region of Republic of colombia (predominantly plains). Information technology suggests dividing the country into four geographic regions: the Andean highlands, consisting of the three Andean ranges and intervening valley lowlands; the Caribbean lowlands coastal region; the Pacific lowlands coastal region, separated from the Caribbean lowlands past swamps at the base of the Isthmus of Panama; and eastern Colombia, the dandy plain that lies to the due east of the Andes Mountains.

The chief western mountain range, the Cordillera Occidental, is a moderately high range with peaks reaching up to about 15,000 ft (4,572 chiliad) (four,670 m).[v] The Cauca River Valley, an important agronomical region with several large cities on its borders, separates the Cordillera Occidental from the massive Cordillera Key. Several snowfall-clad volcanoes in the Cordillera Cardinal have summits that rise above 17,000 ft (5,182 one thousand). The valley of the slow-flowing and muddy Magdalena River, a major transportation avenue, separates the Cordillera Cardinal from the chief eastern range, the Cordillera Oriental. The peaks of the Cordillera Oriental are moderately high. This range differs from Colombia's other mountain ranges in that it contains several large basins. In the east, the sparsely populated, apartment to gently rolling eastern lowlands called llanos cover virtually lx percent of the state's full country surface area.
This cantankerous section of the republic does non include 2 of Republic of colombia'south regions: the Caribbean coastal lowlands and the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta, both in the northern part of the land. The lowlands in the w are mostly swampy; the reed-filled marshes of the area are called ciénagas by the people of Colombia. The Guajira Peninsula in the east is semiarid and is occupied primarily past indigenous peoples. The Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta is a spectacular triangular snowcapped block of rock that towers over the eastern part of this lowland. Here tin be found the highest meridian of the land, named Pico Cristobal Colon (5775 m).[five]
Andean region [edit]


Near the Ecuadorian frontier, the Andes Mountains split into three distinct, roughly parallel bondage, called cordilleras, that extend northeastward well-nigh to the Caribbean Ocean. Altitudes reach more than xviii,700 ft (5,700 thousand), and mountain peaks are permanently covered with snow. The elevated basins and plateaus of these ranges accept a moderate climate that provides pleasant living conditions and in many places enables farmers to harvest twice a year. Torrential rivers on the slopes of the mountains produce a large hydroelectric power potential and add together their book to the navigable rivers in the valleys. In the late 1980s, approximately 78 percent of the country's population lived in the Andean highlands.
The Cordillera Occidental in the west, the Cordillera Central in the eye, and the Cordillera Oriental in the east have different characteristics. Geologically, the Cordillera Occidental and the Cordillera Central form the western and eastern sides of a massive crystalline arch that extends from the Caribbean lowlands to the southern edge of Republic of ecuador. The Cordillera Oriental, yet, is composed of folded stratified rocks overlying a crystalline core.
The Cordillera Occidental is relatively low and is the to the lowest degree populated of the 3 cordilleras. Summits are only about 9,840 ft (two,999 grand) to a higher place sea level and do not have permanent snows. Few passes be, although i that is about 4,985 ft (1,519 m) to a higher place sea level provides the major urban center of Cali with an outlet to the Pacific Body of water. The relatively low top of the cordillera permits dense vegetation, which on the western slopes is truly tropical.
The Cordillera Occidental is separated from the Cordillera Key past the deep rift of the Cauca Valley. The Río Cauca rises within 124 mi (200 km) of the edge with Republic of ecuador and flows through some of the best farmland in the land. After the ii cordilleras converge, the Cauca Valley becomes a deep gorge reaching to the Caribbean area lowlands.
The Cordillera Fundamental is the loftiest of the mountain systems. Its crystalline rocks course a towering wall dotted with snow-covered volcanoes that is 500 mi (805 km) long. There are no plateaus in this range and no passes under 10,825 ft (3,299 m). The highest peak in this range, the Nevado del Huila, reaches 17,602 ft (5,365 thou) to a higher place sea level. The second highest height is a volcano, Nevado del Ruiz, which erupted violently on November 13, 1985. Toward its northern terminate, this cordillera separates into several branches that descend toward the Caribbean area coast.
Betwixt the Cordillera Central and the Cordillera Oriental flows the Magdalena River. This i,600-kilometre-long (994 mi) river rises near a point some 180 km (112 mi) northward of the border with Ecuador, where the Cordillera Oriental and the Cordillera Central diverge. Its spacious drainage area is fed past numerous mountain torrents originating high in the snowfields. The Magdalena River is mostly navigable from the Caribbean Ocean as far equally the boondocks of Neiva, deep in the interior, but it is interrupted midway by rapids. The valley flooring is very deep; about 800 km (497 mi) from the river'southward mouth the superlative is no more than about 300 meters (984 ft).
In the Cordillera Oriental, at elevations between 2,500 and ii,700 meters (8,202 and 8,858 ft), three large fertile basins and a number of small ones provide suitable areas for settlement and intensive economic product. In the bowl of Cundinamarca, where the Spanish encountered the regional Chibcha Indians, the European invaders established the boondocks of Santa Fe de Bogotá (present-day Bogotá) at an tiptop of 2,650 meters (8,694 ft) higher up sea level.
To the north of Bogotá, in the densely populated basins of Chiquinquirá and Boyacá, are fertile fields, rich mines, and large industrial establishments that produce much of the national wealth. Nonetheless further due north, where the Cordillera Oriental makes an abrupt plough to the northwest virtually the border with Venezuela, the Sierra Nevada de Cocuy, the highest point of this range, rises to five,493 meters (18,022 ft) above sea level. In the department of Santander, the valleys on the western slopes are more spacious, and agriculture is intensive in the area around Bucaramanga. The northernmost region of the range around Cúcuta is then rugged that historically it has been easier for residents here to maintain communications and transportation with Venezuela than with the adjacent parts of Republic of colombia.
The bones plantation of Colombia is grassy and is near the equator which allows many tropical-similar plants.
Caribbean area region [edit]

The Caribbean area lowlands consist of all of Republic of colombia north of an imaginary line extending northeastward from the Golfo de Urabá to the Venezuelan frontier at the northern extremity of the Cordillera Oriental. The semiarid Guajira Peninsula and Guajira–Barranquilla xeric scrub, in the extreme n, bear little resemblance to the rest of the region. In the southern part rises the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta, an isolated mountain system with peaks reaching heights over 5,700 meters (18,701 ft) and slopes mostly too steep for cultivation.
The Caribbean area lowlands region is in roughly the shape of a triangle, the longest side of which is the coastline. Nigh of the country's commerce moves through the cities of Cartagena, Barranquilla, Santa Marta, and the other ports located along this of import declension. Inland from these cities are swamps, hidden streams, and shallow lakes that support assistant and cotton plantations for major commodity crops, endless small-scale farms, and, in higher places, cattle ranches.
The city of Cartagena is a petrochemical, seaport (#one in the country), and tourist city (#ane in the country). Santa Marta is likewise a seaport and tourist metropolis simply it is smaller calibration city in comparison. Barranquilla is located some 25 miles (40 km) from the Caribbean coastline just it is a more adult urban center, with a greater number of industries and commercial places, widely known for its skilled workers in producing all forms of metalwork and accomplishing structure. Its inhabitants have the highest pedagogy level of the region. The city is famous equally the starting point and focus of the region and the country's development: it was the get-go metropolis in the nation to install and apply telephones, public lighting, air mail service, planes, and industrial works.
The Caribbean region merges side by side to and is continued with the Andean highlands through the two slap-up river valleys. Afterwards the Andean highlands, it is the 2nd-most important region in terms of economic activeness. Approximately 17% of the country's population lived in this region in the late 1980s.
The region also includes the peninsular archipelago of San Andres Island and the Insular Territories of Colombia, which are disputed in part by Nicaragua. Even so, the Colombian Navy protects such territories with the utilize of force when necessary to avoid strange invasion. The islands are fortified with ii important bases for defense and custom controls. These were formerly used for research of classified projects with civilian assistance; the local universities ofttimes behave research in the areas of oceanography and marine biology but also in the fields of biochemistry, genetics and immunology. Colombia is known for its advances in medical fields in experimental surgery, breast implant development, or prosthetics, and immunology. These facilities serve as containment and secure experimentation labs to complement those in Barranquilla and other undisclosed locations within the coast territories.
The Insular Region is considered by some every bit a geopolitical region of Republic of colombia. It comprises the areas exterior the continental territories of Republic of colombia and includes the San Andrés y Providencia Department in the Caribbean body of water and the Malpelo and Gorgona islands in the Pacific Ocean. Its subregions include other groups of islands:
- Archipiélago de San Bernardo (in the Morrosquillo Gulf, Caribbean area).
- Islas del Rosario (Caribbean area)
- Isla Fuerte (Caribbean)
- Isla Barú (Caribbean)
- Isla Tortuguilla (Caribbean)
- Isla Tierra Bomba (Caribbean)
Pacific region [edit]
The western third of the state is the most geographically complex. Starting at the shore of the Pacific Ocean in the westward and moving eastward at a latitude of 5 degrees north, a diverse sequence of features is encountered. In the extreme west are the very narrow and discontinuous Pacific littoral lowlands, which are backed by the Serranía de Baudó, the lowest and narrowest of Colombia's mount ranges. Next is the wide region of the Río Atrato/Río San Juan lowland.
In 1855, William Kennish, an engineer and veteran of the British Royal Navy, who had immigrated to the United States and was working for a New York City firm, studied the expanse and proposed an inter-oceanic river aqueduct and tunnel to connect the Rio Atrato, with its mouth at the Atlantic Ocean, with tributaries and through a tunnel and aqueduct through Nerqua Pass, to catamenia into Bahía Humboldt at the Pacific Ocean.[six] [7] [8]
This was his alternative to the canal that was eventually built further west on the isthmus of what became Panama after it gained independence in the early 20th century. Although the US sent an expedition to explore Kennish'southward proposal, the concept was not developed at the fourth dimension. Colombia refused a subsequently US offer to build a canal. After independence, in 1903 Panama fabricated a treaty with the US to support structure of the Panama Canal. Colombia occupies well-nigh of the Andes mountain range northern extremity, sharing a bit with Venezuela; the range splits into three branches between the Colombia-Ecuador border.
In the 1980s, only three percent of all Colombians resided in the Pacific lowlands, a region of jungle and swamp with considerable only piffling-exploited potential in minerals and other resources. Later in the 20th century, information technology was threatened by mining-related deforestation, as gold mining proceeded by both major companies and artisan miners. Buenaventura is the simply port of any size on the coast. To the e, the Pacific lowlands are bounded past the Cordillera Occidental, from which numerous streams run. Most of the streams flow westward to the Pacific, just the largest, the navigable Río Atrato, flows northward to the Golfo de Urabá. Its river settlements have access to the major Atlantic ports and consequently are commercially related primarily to the Caribbean area lowlands hinterland. To the west of the Río Atrato rises the Serranía de Baudó, an isolated chain of depression mountains that occupies a large part of the region. Its highest peak is less than 1,800 meters, and its vegetation resembles that of the surrounding tropical forest.
The Atrato Swamp, in Chocó Department adjoining the border with Panama, is a deep muck sixty-five kilometers in width. For years it has challenged engineers seeking to consummate the Pan-American Highway. This stretch, about Turbo, where the highway is interrupted, is known as the Tapón del Chocó (Chocon Plug).
A 2d major transportation projection in Chocó Section has been proposed. A second inter-oceanic culvert would be constructed by dredging the Río Atrato and tributary streams and digging short access canals. Completion of either of these projects would exercise much to transform this region, although it could have devastating consequences on the frail, tropical forest environment.
Orinoquía region [edit]
The area east of the Andes includes about 699,300 foursquare kilometers or three-fifths of the country's full surface area, but Colombians view it almost as an alien state. The entire area, known equally the eastern plains, was home to just two percentage of the country'due south population in the late 1980s. The Spanish term for plains (llanos) can be applied only to the open up plains in the northern function, particularly the Piedmont areas near the Cordillera Oriental, where extensive cattle raising is practiced.
The region is unbroken past highlands except in Meta Department, where the Serranía de la Macarena, an outlier of the Andes has unique vegetation and wildlife believed to exist reminiscent of those that once existed throughout the Andes.
Amazon region [edit]
Many of the numerous big rivers of eastern Colombia are navigable. The Río Guaviare and the streams to its north period eastward and drain into the basin of the Río Orinoco, a river that crosses into Venezuela and flows into the Atlantic Ocean. Those due south of the Río Guaviare flows into the Amazon Basin. The Río Guaviare divides eastern Republic of colombia into the llanos subregion in the north and the tropical rainforest, or selva, subregion in the south.
Climate [edit]


Flooding in Colombia, Apr 2004
The striking diversity in temperature and precipitation results principally from differences in acme. Temperatures range from very hot at sea level to relatively common cold at higher elevations only vary picayune with the season. At Bogotá, for example, the average almanac temperature is 15 °C (59 °F), and the difference between the average of the coldest and the warmest months is less than one °C (ane.8 °F). More pregnant, still, is the daily variation in temperature, from 5 °C (41 °F) at night to 17 °C (62.six °F) during the mean solar day.
Colombians customarily draw their land in terms of the climatic zones: the area under 900 meters (ii,953 ft) in top is chosen the hot zone (tierra caliente), elevations betwixt 900 and 1,980 meters (2,953 and 6,496 ft) are the temperate zone (tierra templada), and elevations from 1,980 meters (half-dozen,496 ft) to virtually three,500 meters (11,483 ft) constitute the cold zone (tierra fría). The upper limit of the cold zone marks the tree line and the approximate limit of human habitation. The treeless regions next to the cold zone and extending to approximately iv,500 meters (14,764 ft) are high, bleak areas (commonly referred to as the páramos), in a higher place which begins the surface area of permanent snow (nevado).
About 86% of the state'southward total area lies in the hot zone. Included in the hot zone and interrupting the temperate surface area of the Andean highlands are the long and narrow extension of the Magdalena Valley and a small extension in the Cauca Valley. Temperatures, depending on acme, vary between 24 and 38 °C (75.ii and 100.four °F), and there are alternate dry and wet seasons corresponding to summer and winter, respectively. Breezes on the Caribbean coast, nevertheless, reduce both heat and precipitation.
Rainfall in the hot zone is heaviest in the Pacific lowlands and in parts of eastern Colombia, where rain is nigh a daily occurrence and rain forests predominate. Precipitation exceeds 7,600 millimeters (299.2 in) annually in most of the Pacific lowlands, making this one of the wettest regions in the world. The highest average almanac precipitation in the world is estimated to be in Lloro, Republic of colombia, with 13,299 mm (523.six in).[ix] In eastern Colombia, information technology decreases from 6,350 millimeters (250 in) in portions of the Andean Piedmont to 2,540 millimeters (100 in) eastward. All-encompassing areas of the Caribbean interior are permanently flooded, more because of poor drainage than considering of the moderately heavy precipitation during the rainy flavour from May through October.
The temperate zone covers about 8% of the country. This zone includes the lower slopes of the Cordillera Oriental and the Cordillera Central and nigh of the intermontane valleys. The important cities of Medellín (1,487 meters or 4,879 feet) and Cali (1,030 meters or iii,379 feet) are located in this zone, where rainfall is moderate and the mean annual temperature varies between xix and 24 °C (66.two and 75.2 °F), depending on the elevation. In the college elevations of this zone, farmers benefit from two wet and two dry seasons each twelvemonth; January through March and July through September are the dry out seasons.

The cold or cool zone constitutes nearly 6% of the total expanse, including some of the most densely populated plateaus and terraces of the Colombian Andes; this zone supports almost one 4th of the country's total population. The mean temperature ranges between 10 and nineteen °C (fifty.0 and 66.two °F), and the wet seasons occur in April and May and from September to December, as in the high elevations of the temperate zone.
Atmospheric precipitation is moderate to heavy in nearly parts of the country; the heavier rainfall occurs in the low-lying hot zone. Considerable variations occur because of local atmospheric condition that bear upon current of air currents, nonetheless, and areas on the leeward side of the Guajira Peninsula receive generally light rainfall; the annual rainfall of 350 millimeters (13.viii in) recorded at the Uribia station there is the lowest in Colombia. Considerable year-to-twelvemonth variations have been recorded, and Republic of colombia sometimes experiences droughts.
Colombia's geographic and climatic variations have combined to produce relatively well-defined "ethnocultural" groups among different regions of the land: the Costeño from the Caribbean declension; the Caucano in the Cauca region and the Pacific coast; the Antioqueño in Antioquia, Caldas, Risaralda, and Valle del Cauca departments; the Tolimense in Tolima and Huila departments; the Cundiboyacense in the interior departments of Cundinamarca and Boyacá in the Cordillera Oriental; the Santandereano in Norte de Santander and Santander departments; and the Llanero in the eastern plains. Each grouping has distinctive characteristics, accents, community, social patterns, and forms of cultural adaptation to climate and topography that differentiates information technology from other groups. Fifty-fifty with rapid urbanization and modernization, regionalism and regional identification continued to be of import reference points, although they were somewhat less prominent in the 1980s than in the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries.
Colombia's proximity to the equator influences its climates. The lowland areas are continuously hot. Distance affects temperature greatly. Temperatures decrease almost 3.five °F (ane.nine °C) for every ane,000-human foot (305 one thousand) increment in altitude to a higher place sea level. Rainfall varies past location in Republic of colombia, disposed to increase as ane travels southward. This is specially true in the eastern lowlands. For example, rainfall in parts of the Guajira Peninsula seldom exceeds thirty in (762 mm) per year. Colombia's rainy southeast, however, is often drenched by more than 200 in (5,080 mm) of rain per year. Rainfall in well-nigh of the rest of the country runs between these ii extremes.
Vegetation [edit]

Distance affects not but temperature, simply also vegetation. In fact, distance is one of the well-nigh important influences on vegetation patterns in Republic of colombia. The mountainous parts of the country can be divided into several vegetation zones according to altitude, although the altitude limits of each zone may vary somewhat depending on the latitude.
The "tierra caliente" (hot land), below 1,000 k (3,300 ft), is the zone of tropical crops such equally bananas. The tierra templada (temperate land), extending from an altitude of 1,000 to ii,000 k (3,300 to 6,600 ft), is the zone of java and maize. Wheat and potatoes dominate in the "tierra fría" (cold land), at altitudes from 2,000 to 3,200 m (six,600 to 10,500 ft). In the "zona forestada" (forested zone), which is located between iii,200 and 4,000 g (x,500 and xiii,100 ft), many of the trees have been cut for firewood. Treeless pastures dominate the páramos, or tall grasslands, at altitudes of 4,000 to four,500 chiliad (13,100 to 14,800 ft). Above 4,500 m (14,800 ft), where temperatures are beneath freezing, is the "tierra helada", a zone of permanent snowfall and ice.
Vegetation too responds to rainfall patterns. A scrub woodland of scattered trees and bushes dominates the semiarid northeast. To the south, savannah (tropical grassland) vegetation covers the Colombian portion of the llanos. The rainy areas in the southeast are blanketed by tropical rainforest. In the mountains, the spotty patterns of atmospheric precipitation in tall areas complicate vegetation patterns. The rainy side of a mountain may exist lush and green, while the other side, in the rain shadow, may be parched.
Relief [edit]

The Andean range is located in Colombia from the southwest (Ecuador border) toward the northeast (Venezuela border) and is divided in the Colombian Massif (Macizo Colombiano) in 3 ranges (Eastward Andes, Central Andes and West Andes) that class two long valleys, Magdalena and Cauca follow by the rivers of the same proper noun.
The eastern one-half of Colombia, comprising more than half its territory, is plain and composed by savanna and rainforest, crossed by rivers belonging to the Amazon and Orinoco basins. The northern part, chosen the Llanos, is a savanna region, mostly in the Orinoco basin (therefore chosen as well Orinoquía). The southern role is covered by the Amazon pelting forest and belongs by and large to the Amazon bowl. It is unremarkably called Amazonía.
At the north and west of the Andes range there are some coastal plains. The Caribbean plains at the north and the Pacific plains at the westward.
A contempo global remote sensing analysis suggested that there were 553km² of tidal flats in Colombia, making information technology the 46th ranked country in terms of tidal flat expanse.[10]
Colombian Pacific Plains are among the most rainy parts in the world, importantly at the north (Chocó).
The highest mount in Republic of colombia is not in the Andes but in the Caribbean area evidently: Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta with its highest points named Pico Cristobal Colon (5775 chiliad) and Pico Simon Bolivar (aforementioned elevation). Other mountains in the Caribbean area manifestly include the Montes de María and the Serranía de San Lucas.
In the Pacific Plains there are other mountain formations, chiefly the Serranía del Darién and the Serranía del Baudó.
In the eastern Region, in that location is the Serranía de la Macarena and in that location are formations belonging to the Republic of guyana Shield.
Protected areas [edit]

National natural parks of Colombia.
Natural resource [edit]
The natural resources of Colombia are varied and extensive with most of its territory and oceans all the same unexplored. Colombia has i of the largest open pit coal mines in the world in the region of Cerrejon in the Guajira Peninsula. It also has oil rigs and natural gas extraction in the eastern plains. Republic of colombia is the primary producer of emeralds and an important participant in gold, silver, iron, table salt, platinum, petroleum, nickel, copper, hydropower and uranium extraction.[11]
Environmental problems [edit]

State employ map of Colombia, 1970.
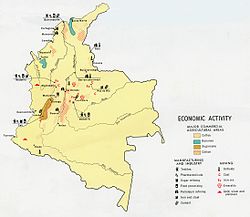
Economic activity map of Colombia, 1970.
The main environmental issues affecting Colombia are deforestation; soil and water quality impairment from overuse of pesticides; air pollution, especially in Bogota, from vehicle emissions and other main cities. The collateral damaged produced by attacks against oil pipeline infrastructure by rebel guerrillas in the Colombian armed conflict has produced long term damage to the environment. The armed groups also deforest large areas to cultivate illegal crops and open unauthorized highways in protected areas.
Farthermost points [edit]
- Highest points
Snowfields and glaciers in Colombia are limited to the highest peaks and ranges in the Cordillera Central and Cordillera Oriental and above the four,700-metre (fifteen,400 ft) elevation on the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta. The total expanse of snowfields and glaciers was estimated to be virtually 104 foursquare kilometers in the early 1970s.
Historical, geographical, and pictorial records betoken toward a consistent and progressive depletion of water ice-and-snow masses in the Colombian Andes since the cease of the "Little Ice Historic period" in the late 1800s. Many glaciers have disappeared during the 20th century, and others are expected to disappear in the coming decades.[12]
Facts [edit]
State size: full: 1,138,910 km2 (439,740 sq mi)
Land boundaries: full: 6,672 km
Coastline: 3,208 km (Caribbean Sea one,760 km, N Pacific Ocean 1,448 km)
Sectional Economic Zone: total: 808,158 kmtwo (312,032 sq mi)
Climate: tropical along declension and eastern plains; libation in highlands
Terrain: apartment coastal lowlands, central highlands, high Andes Mountains, eastern lowland plains
Elevation extremes: lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m highest signal: Pico Cristobal Colon 5,975 m annotation: nearby Pico Simon Bolivar besides has the same summit
Natural resources: petroleum, natural gas, coal, fe ore, nickel, gold, copper, emeralds, hydropower
Land utilise: abundant state: ane.43% permanent crops: 1.68% other: 96.89% (2012)
Irrigated land: x,870 km2 (2011)
Full renewable water resources: 2,132 km3 (2011)
Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural): total: 12.65 kmiii (55%/4%/41%) per capita: 308 miii/twelvemonth (2010)
Natural hazards: highlands subject to volcanic eruptions; occasional earthquakes; periodic droughts
Surround - international agreements: political party to: Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Transport Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands signed, just non ratified: Police of the Ocean
Hydrology [edit]
Colombia has four main drainage systems: the Pacific drain, the Caribbean area bleed, the Orinoco Basin and the Amazon Basin.
The Orinoco and Amazon Rivers marking limits with Colombia to Venezuela and Peru respectively.
| Caribbean Drain | Pacific Drain | Orinoco Basin | Amazon Basin |
|---|---|---|---|
Rivers confined to Colombia [edit] | |||
|
|
|
|
Rivers originating in Colombia [edit] | |||
|
|
| |
Lakes [edit]

- Ciénaga Grande de Santa Marta
- La Cocha Lagoon
- Lake Tota
Encounter also [edit]
- Environmental issues in Colombia
References [edit]
- ^ "The Republic of colombia shares country borders with five (5) countries". cancilleria.gov.co.
- ^ "Maritime borders". cancilleria.gov.co.
- ^ (in Castilian) UNAL: History of the Colombian electric current territory [ permanent expressionless link ] UNAL Accessed 23 August 2007.
- ^ DANE: 2005 Census of Republic of colombia - total area Archived 2013-04-03 at the Wayback Automobile dane.gov.co Accessed 23 August 2007.
- ^ a b "Travel map of the Andes". Nelles Map. Archived from the original on 2010-09-24. Retrieved 2011-01-10 .
- ^ Page of The Practicality and Importance of a Ship Canal to Connect the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans.
- ^ Kennish, W. (c. 1855). "Interoceanic river aqueduct connecting the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans: [Republic of colombia] (map)". Library of Congress. Retrieved 6 Apr 2020.
- ^ Kennish, Due west. (1855). "Birds eye view of the pass of the intero-ceanic river channel and valley of the Nerqua". Library of Congress. Retrieved 7 April 2020.
- ^ Global Measured Extremes of Temperature and Atmospheric precipitation. National Climatic Data Center. Baronial 9, 2005. Terminal accessed Jan 18, 2007.
- ^ Murray, N.J.; Phinn, S.R.; DeWitt, M.; Ferrari, R.; Johnston, R.; Lyons, G.B.; Clinton, N.; Thau, D.; Fuller, R.A. (2019). "The global distribution and trajectory of tidal flats". Nature. 565: 222–225. doi:10.1038/s41586-018-0805-8.
- ^ Encyclopedia Encarta: Natural Resources of Republic of colombia Encyclopedia Encarta Accessed 24 August 2007. Archived 2009-01-31 at the Wayback Machine 2009-ten-31.
- ^ USGS: Glaciers of Colombia USGS Accessed 23 August 2007.
External links [edit]
- Colombian Ministry of Environs (in Spanish)
- Map of the Republic of Colombia from 1891 (in English language)
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Geography_of_Colombia